While blue teams defend, red teams attack. However, they share a common goal: to help identify and address holes in organizations’ defenses before these weaknesses can be exploited by malicious actors. The Blue/Red team exercises provide invaluable insights into the technical, procedural and human sides of security and can ultimately help organizations fend off actual attacks.
We recently looked at some open source tools that blue teams can use to defend against simulated attacks, as well as four gadgets that could cause security issues in the wrong hands. This time we round up five advanced, compact tools that hobbyist hardware hackers, red teamers or ethical hackers alike can use while sharpening their skills or doing their job.
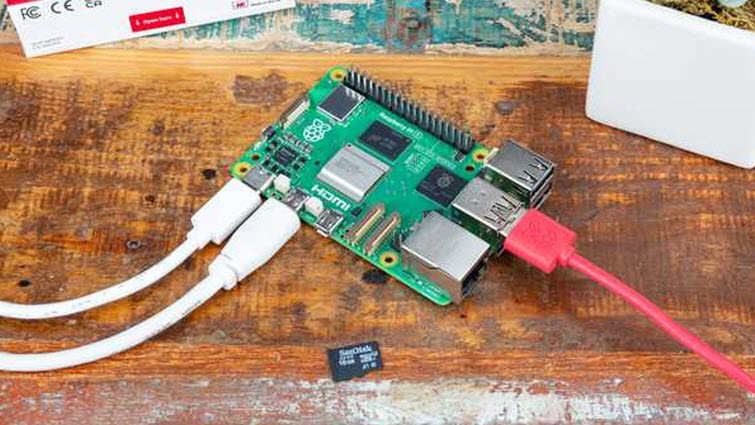
1. Raspberry Pi 5
Thanks largely to its versatility, power and vibrant community-driven ecosystem, the Raspberry Pi has become a favorite tool among security professionals, students and enthusiasts. The Raspberry Pi is primarily an affordable single-board computer, but it can also be equipped with various penetration testing tools and serve multiple roles.
For example, it can ‘turn’ into a network sniffer and capture packets for detailed analysis or run scripts for automated security testing. It is also ideal for testing tools on the go and analyzing Internet of Things (IoT) devices, identifying vulnerabilities before cybercriminals have a chance to exploit them.
The Raspberry Pi supports a variety of operating systems tailored to different purposes and user preferences. The official operating system, Raspberry Pi OS (formerly Raspbian), is based on Debian Linux and is optimized for the ARM architecture.
Moreover, there are popular distributions like Kali Linux available, and they are specifically made for penetration testing and security auditing. These distributions come pre-loaded with a range of tools for network scanning, vulnerability assessment, wireless attacks and more.
Here are also a few interesting tools and projects that can use Raspberry Pi as an underlying hardware platform:
- FruityWifi: Used to monitor wireless networks and enable advanced attacks through a web interface.
- Ha-Pi: Offers penetration testing tools including Aircrack Ng Suite and Metasploit.
- Raspberry Pwn: Includes tools such as scapy, Wireshark and tcpdump.
- Wireless Attack Toolkit (WAT): Performs Wi-Fi network penetration testing on ARM platforms.
- PwnPi: A simplified version of Debian Wheezy for pen testing.
- NetPi: A project aimed at creating a network analyzer with commercial functions.
2. HackRF One
The HackRF One is a Swiss army knife for radio frequency (RF) enthusiasts and professionals alike. This open source device allows anyone from curious hobbyists to seasoned professionals to dive into the invisible ocean of RFs and explore and manipulate the waves that carry everything from your favorite music station to critical communications signals.
This single-board software-defined radio peripheral (SDR) is designed to be versatile and can both send and receive signals from 1 MHz to 6 GHz. This enormous range allows you to experiment with virtually any type of wireless communication, from AM/FM radio to Wi-Fi and even satellite signals. It’s almost like having the keys to every wireless protocol ever devised, all in one compact form factor.
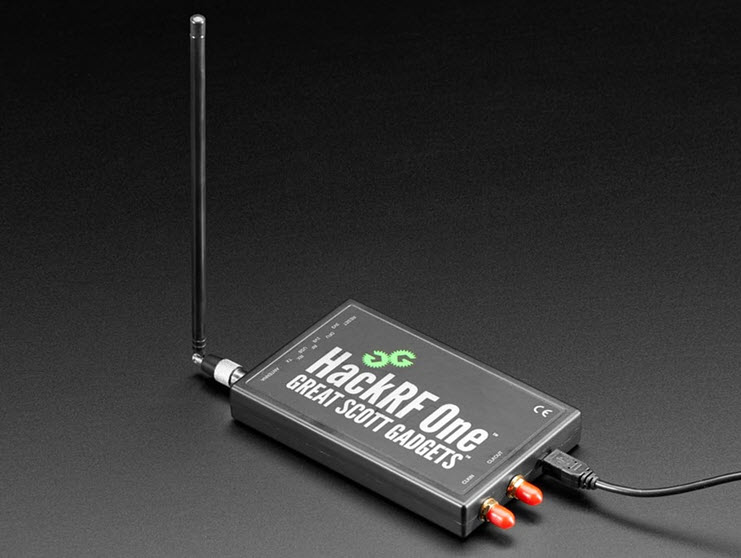

Despite its advanced capabilities, HackRF One is portable and rugged enough for field work, allowing security professionals to test vulnerabilities in wireless networks or RF technicians to troubleshoot signal issues on the go.
Speaking of which, you can use it to assess the security of wireless systems, conduct replay attacks, and investigate the vulnerabilities of IoT devices. This includes emulating and analyzing car remote controls, alarms and other devices, manipulating GPS signals, communicating with RFID tags, and performing signal analysis and tracking of satellite communications.
3. WiFi Pineapple
Granted, you might need a bigger pocket for this, but this sleek gadget that looks like an innocuous router has the power to reveal the hidden secrets of wireless networks. The WiFi Pineapple is used to investigate the security of wireless networks by simulating a conventional access point where it attracts unsuspecting users. It has two network interfaces: one for providing Internet access and the other for interacting with nearby Wi-Fi devices.
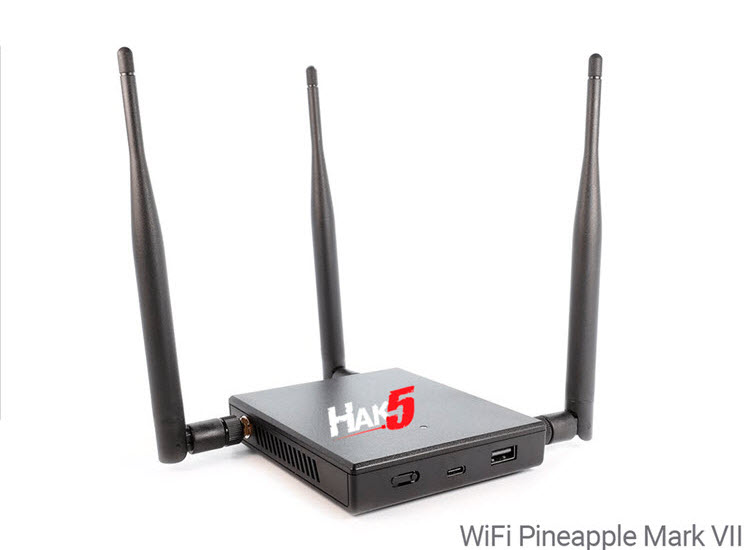

At the heart of the WiFi Pineapple is its custom operating system, Pineapple OS. This Linux-based operating system is specifically intended for wireless penetration testing and comes pre-loaded with a plethora of powerful tools. Pineapple OS provides a stable and efficient environment, allowing the device to function smoothly during complex security assessments.
Main purposes:
- Evil Double Attacks: Creates fraudulent access points to intercept network traffic and collect sensitive information.
- Death Tests: Forces disconnections from legitimate networks to enable man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Security Ratings: Identifies vulnerabilities and configuration gaps in wireless networks.
- Controlled attacks: Helps administrators understand and develop better security policies.
- Versatile functionality: Offers various automated and manual pen testing tools for wireless networks.
4. Deauther watch
The name says it all. This gadget is essentially a wearable that integrates capabilities for carrying out Wi-Fi deauthentication attacks. It disrupts the Wi-Fi connection between a device (such as a smartphone, laptop, or IoT device) and a Wi-Fi router by sending specially crafted deauthentication packets.

Additionally, the Deauther Watch can come with features such as Wi-Fi scanning and monitoring, and packet logging to detect vulnerabilities or monitor network activity. The ESP8266 Deauther V3 software provides a command line interface (CLI) via USB and tests 2.4 GHz WiFi networks for vulnerabilities.
5. Ubertooth One
The Ubertooth One is primarily designed for monitoring Bluetooth communications and analyzing Bluetooth packets, as well as testing Bluetooth-enabled Internet of Things (IoT) devices. This open-source gadget supports various security testing scenarios, including detecting sensitive information exchanged over Bluetooth connections. Its capabilities go even beyond typical Bluetooth adapters and can be customized to meet specific security testing needs.
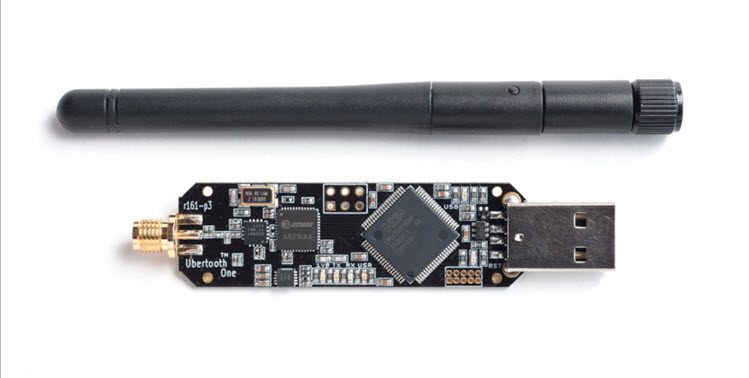
It is based on the GreatFET platform and features a capable radio transceiver chipset. The Ubertooth One operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band and supports Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and Classic Bluetooth protocols, making it versatile enough to tackle a wide range of applications.
Conclusion
As with all these types of gadgets, ethical considerations are paramount. The technology should be used in environments and situations where consent is given, such as in controlled testing environments or for educational purposes. Using it to carry out unapproved attacks is illegal in many jurisdictions and can have serious consequences. In the meantime, organizations must implement a combination of technical measures, policies and user education so that they remain protected against unauthorized use of these devices on their networks.





















